How Can Women Use Swimming to Improve Posture? (2024)
- Updated:
Maintaining good posture is crucial for overall health and well-being. Poor posture can lead to discomfort, pain, and a range of other health issues. Swimming offers a fun and effective solution for women looking to improve posture. This article explores how swimming can enhance posture, the mechanics behind it, and practical tips for integrating swimming into your routine.
Why is Posture Important?
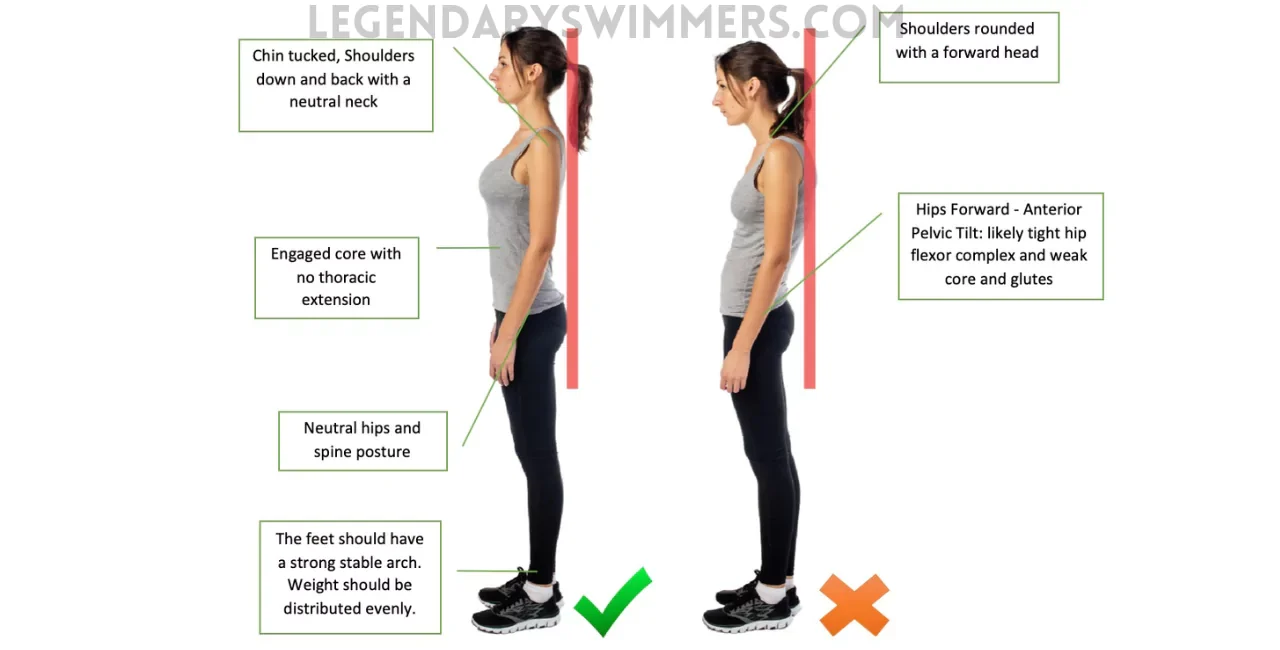
Poor posture can lead to musculoskeletal problems such as chronic back pain, shoulder tension, and joint issues. According to the American Chiropractic Association, 80% of people will experience back pain at some point in their lives, often exacerbated by poor posture.
Good posture is linked to better mental health. A study published in “Health Psychology” found that adopting an upright posture can boost mood and increase feelings of power and confidence.
Proper posture facilitates optimal lung capacity and efficient breathing. Slouching compresses the chest, limiting airflow and potentially leading to respiratory issues.
How Swimming Benefits Posture
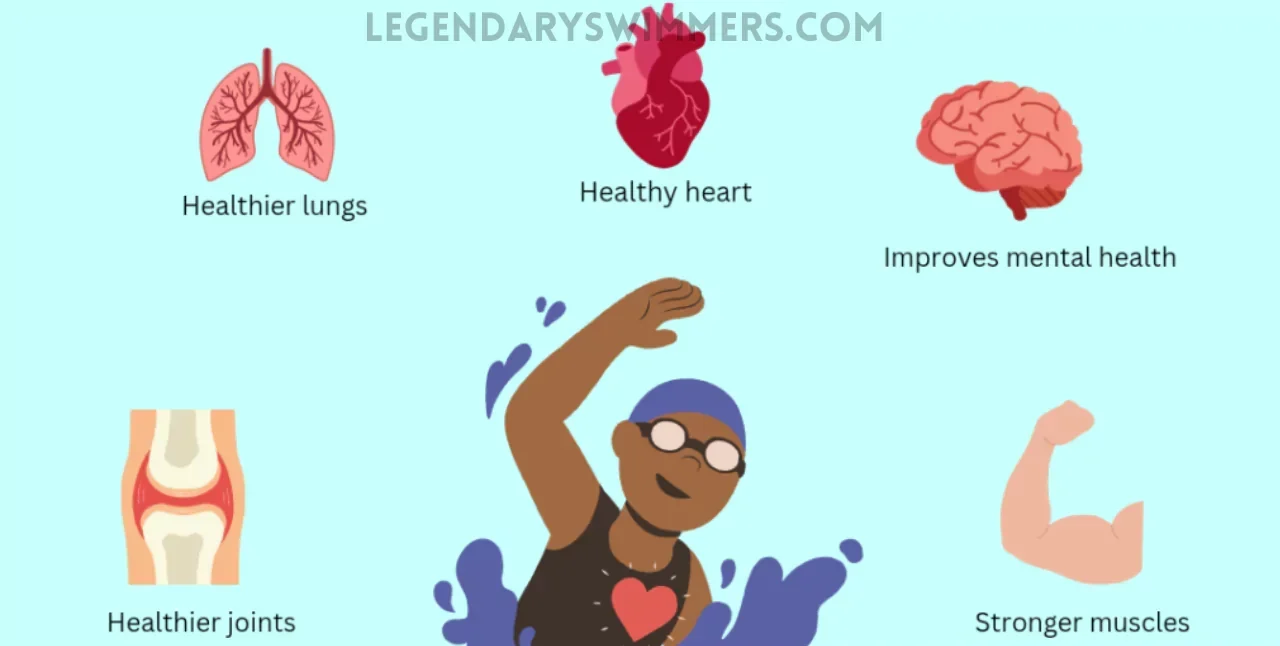
Swimming offers a range of benefits for posture, going beyond just muscle engagement and flexibility. Let’s explore these aspects more deeply by incorporating user experiences and expert insights into the discussion.
Muscle Engagement and Its Impact on Posture
Many women who swim regularly report significant improvements in their posture due to the strengthening of core muscles. These muscles are vital for maintaining stability and balance, both in and out of the water.
For example, experienced swimmers often notice that their abdominal and lower back muscles become stronger after consistent practice. This is essential for posture because the core acts as the body’s support system. By engaging the core muscles during various swimming strokes, women can correct the forward-leaning posture that can result from hours of sitting at a desk.
Expert opinion supports this observation. According to physiotherapists, core muscle engagement is critical for spinal stability. The resistance provided by water adds an extra layer of intensity to core workouts without the strain of traditional land-based exercises. “Water’s resistance helps in activating deep core muscles that are often neglected in regular workouts,” says Jane Adams, a certified swim coach and physiotherapist.
Upper and Lower Body Muscles:
One of the most noticeable user experiences from swimming is the toning of both the upper and lower body muscles. Women frequently report that strokes like backstroke and freestyle not only work the large muscle groups, like the shoulders and thighs, but also smaller stabilizing muscles that contribute to overall body alignment. This balanced muscle development can correct imbalances that cause slouching or uneven posture.
According to a report by the American College of Sports Medicine, regular swimmers tend to develop proportional strength across their bodies, which helps improve posture more effectively than some other forms of exercise. Upper-body strokes, particularly freestyle, engage the latissimus dorsi (the large back muscles) and shoulder stabilizers, while the lower body benefits from the flutter kick. These movements, when done consistently, can help correct rounded shoulders and lower back issues.
Flexibility and Its Role in Posture
Many women experience tightness in the chest and shoulders, especially after spending long periods sitting or working at a computer. Swimming, with its dynamic range of motion, helps alleviate this tension by gently stretching these muscles. Freestyle and backstroke movements, in particular, stretch the pectoral muscles, leading to a more open, upright posture.
From personal accounts, women who swim regularly often say they feel more limber and free from the aches caused by sitting or standing with poor posture for long hours. A competitive swimmer from Sydney shared how daily swimming helped her alleviate years of neck and shoulder tension, which had developed from working long hours at a desk. Her improved posture not only helped her physical health but also boosted her confidence.
Experts in sports medicine agree that flexibility plays a crucial role in posture correction. Dr. Michelle Stone, an orthopedic surgeon, states, “The natural stretching of the body during swimming is ideal for women looking to improve their flexibility. It gently opens up tight muscles, allowing for better posture and less strain on the spine.”
Improved flexibility leads to a greater range of motion in the joints, which is vital for maintaining proper alignment. Stiffness in areas like the hips, shoulders, and neck can force women into poor postural habits, such as slouching or rounding the back. Swimming combats this by promoting full-body stretches with every stroke.
Women who have added swimming to their routines often note that their everyday movements become easier and less strained. For example, one user commented that after three months of swimming, she could stand taller with less effort, and her posture improved, especially during daily activities like lifting objects or walking.
In a study conducted at the University of Sydney, swimmers were found to have significantly higher levels of flexibility compared to those who only performed dry-land exercises. This increased flexibility directly contributed to improved posture and reduced muscle stiffness, particularly in older women or those recovering from injuries.
Balance and Alignment
Unlike exercises on land, where balance can be more challenging due to gravity, water gives a natural support system, allowing swimmers to work on core stability without the risk of falling. As a result, swimmers often report feeling more centered and stable not only in the pool but also in everyday life.
For instance, women who swim regularly note improved balance when performing daily tasks, such as walking or even standing for long periods. This improvement comes from the need to maintain equilibrium in water, which strengthens the small stabilizing muscles in the legs, hips, and core.
Experts like Dr. Sarah Thomas, a sports physiologist, explain that “the resistance in water forces the body to engage muscles continuously to maintain balance, and this can translate to improved coordination and posture on land.” Regular swimming, she notes, can help correct common postural imbalances caused by sedentary lifestyles.
Additional Swimming Exercises for Better Alignment:
Strokes like backstroke and butterfly promote better body alignment and strength. These strokes encourage a straight, elongated body position, reinforcing good posture habits. Women who swim backstroke often feel it helps them achieve better posture by encouraging a straight alignment of the spine.
Although one of the more challenging strokes, the butterfly helps develop a strong core and back muscles. The stroke’s wave-like motion engages the entire body, particularly the shoulders, upper back, and abdominal muscles, which are critical for maintaining good posture.
Water Aerobics
Water aerobics is an excellent complement to swimming, particularly for improving posture. Exercises like water jogging and leg lifts help enhance core strength and flexibility, which are crucial for maintaining good posture. Incorporating posture-focused exercises, such as water planks and bicycle kicks, into a water aerobics routine can further support and improve posture. By targeting the core muscles, these activities help reinforce proper alignment and stability, making water aerobics a valuable addition to any swimming regimen.
Pool Workouts for Core Strength
Specific pool workouts can significantly enhance core stability, which is essential for maintaining good posture. Incorporating exercises like water crunches and leg raises into your routine can effectively strengthen the core muscles that support proper alignment. This combination of swimming and targeted pool exercises provides a comprehensive strategy for developing a strong, stable core and improving overall body alignment.
Practical Tips for Integrating Swimming into Your Routine
For beginners aiming to use swimming to improve posture, it’s essential to start with a structured and gradual approach. Focus on mastering basic strokes like freestyle and backstroke, which help build core stability and strengthen key muscle groups involved in maintaining good posture.
A common beginner mistake is rushing through strokes, which can lead to poor technique and less benefit for posture. Instead, take your time to engage the core, align your body correctly, and focus on steady, controlled movements. To enhance posture, it’s important to maintain body awareness, ensuring the head stays aligned with the spine and the hips remain level throughout the swim.
Recommended Frequency and Duration for Posture Benefits
Consistency is key when it comes to seeing improvements in posture through swimming. For noticeable changes, aim for 2-3 sessions per week, with each session lasting 30-45 minutes. This frequency is manageable for beginners and provides enough time for muscles to recover and adapt between swims.
Those who have implemented this routine often report that even after a few weeks, they experience reduced back pain, greater shoulder flexibility, and improved body alignment.
Experts also recommend incorporating rest days or alternating swimming with other forms of low-impact exercise, such as yoga or Pilates, to prevent overexertion and maintain flexibility.
Combining Swimming with Strength Training
Strength training is another powerful way to complement swimming for posture improvement. Strong muscles act as a support system for maintaining good posture, reducing the strain on joints and ligaments. Women who alternate swimming with strength workouts often experience better postural alignment and less muscle fatigue throughout the day.
Conclusion
Swimming offers a multifaceted approach to improving posture by strengthening core muscles, enhancing flexibility, and promoting balance and alignment. Regular swimming can lead to better posture, reduced back pain, and overall improved well-being.
Incorporating swimming into your fitness routine can make a significant difference in your posture and overall health. Dive into a swimming routine with Legendary Swimmers and experience the benefits for yourself.
FAQs
Q: How often should women swim to see improvements in posture?
A: To see noticeable improvements, aim for 2-3 swimming sessions per week, each lasting 30-45 minutes.
Q: Why does swimming help with posture more than other forms of exercise?
A: Swimming engages multiple muscle groups, promotes flexibility, and supports body alignment, making it an effective exercise for improving posture.
Q: What if I have a pre-existing back condition—can swimming still help?
A: It’s always best for individuals to consult their healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine, especially if they have existing back conditions. Swimming can be a great option for many, but personalized advice is key to ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Q: How can I maintain good posture outside of the pool?
A: Incorporate posture-friendly habits such as sitting with your back straight, using ergonomic furniture, and performing regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
References and Further Reading
Recommended Products:
 FINIS Posture Trainer Head Alignment Swim Training Tool
FINIS Posture Trainer Head Alignment Swim Training Tool
 FINIS Original Center-Mount Swimmer’s Snorkel for Lap Swimming and Swim Training
FINIS Original Center-Mount Swimmer’s Snorkel for Lap Swimming and Swim Training

Natasha Nicole Leyva
Hi, I’m Natasha—swimmer, coach, and aquatic fitness enthusiast. My journey began in New Zealand after a professor recommended swimming to help with a knee injury. The low-impact nature of swimming worked wonders, and it quickly became my favorite form of exercise. This passion grew into a thriving swim academy, and soon, requests for aquatic fitness classes started pouring in. After becoming certified, I realized how powerful water workouts could be for recovery and fitness. Now, I share my expertise here to help others experience the benefits of aquatic movement—whether for recovery, fitness, or fun!







